Chilas Technology: Hybrid-integration external cavity laser (ECL)
Chilas lasers are made with hybrid-integration laser technology. Chilas’ laser comprises an InP reflective semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA) as gain medium and a Si3N4 waveguide circuit as external cavity. The RSOA is edge-coupled to the external cavity. Two coupled micro-ring resonators (MRRs) with slightly different free spectral range (FSR) in the cavity ensure stable single frequency operation due to the Vernier effect. By means of heater elements the micro-ring resonators can be tuned over a 2𝜋 phase shift, permitting the laser to address any wavelength within the gain bandwidth.
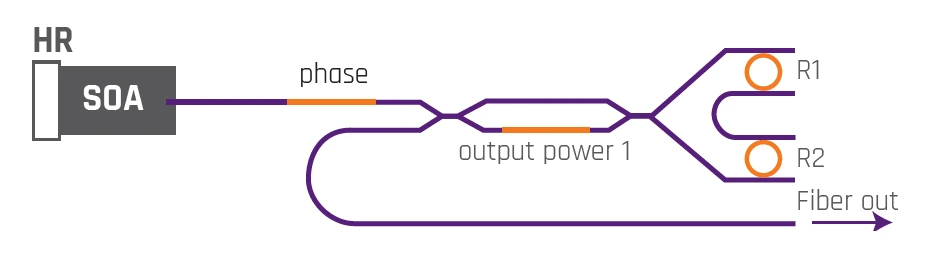
Due to low cavity loss and long optical cavity length, Chilas’ laser can achieve high output power (> 20mW) and ultra-narrow linewidth (< 1kHz).
The lasers come as a standard 14-pin butterfly package, equipped with a Peltier element. The output fiber is PM with a FC/APC connector. Upon request, other packages and fibers can be made available.
Publications
While developing our technology, we contribute to academic conferences by disseminating our latest results. An overview of our recent contributions can be found here.
More in-depth information about our hybrid-integration technology, tuning operation, laser linewidth and different wavelength ranges, can be found in the following journal papers:
• “Hybrid Integrated Semiconductor Lasers with Silicon Nitride Feedback Circuits” K.-J. Boller, et al., Photonics 7(1), 4 (2019), DOI.
• “Widely tunable and narrow-linewidth violet lasers enabled by UV-transparent materials”, C. A. A. Franken, et al., Nat. Commun. 16, 10294 (2025), DOI.
• “Widely tunable and narrow-linewidth hybrid-integrated diode laser at 637 nm”, L. V. Winkler, Opt. Express 32(17), 29710–29720 (2024), DOI.
• “Long-term Absolute Frequency Stabilization of a Hybrid-Integrated InP-Si3N4 Diode Laser”, A. van Rees, et al., IEEE Photonics J. 15(5), 1502408 (2023), DOI.
• “Hybrid-integrated diode laser in the visible spectral range”, C. A. A. Franken, et al., Opt. Lett. 46(19), 4904–4907 (2021), DOI.
• “Hybrid integrated InP-Si3N4 diode laser with a 40-Hz intrinsic linewidth”, Y. Fan, et al, Opt. Express 28(15), 21713–21728 (2020), DOI.
• “Ring resonator enhanced mode-hop-free wavelength tuning of an integrated extended-cavity laser”, A. van Rees, et al., Opt. Express 28(4), 5669–5683 (2020), DOI.
• “Optically Integrated InP-Si3N4 Hybrid Laser”, Y. Fan, et al., IEEE Photonics J. 8(6), 1505111 (2016), DOI.
• “25 kHz narrow spectral bandwidth of a wavelength tunable diode laser with a short waveguide-based external cavity”, R. M. Oldenbeuving, et al., Laser Phys. Lett. 10, 015804 (2013), DOI.
